This article contains informations about Oracle Blockchain Tables and benefits. You will also find information about creating oracle blockchain tables and insert into data to it.
Blockchain is a technology that is actively used now a days. In today’s article, we will talk about some introductory information about Oracle Database and Blockchain.
What is Oracle Blockchain?
“Oracle Blockchain table is currently used only on Oracle Cloud.”
Unlike other structures, the Oracle Blockchain table can be used for blockchain applications where the central authority is Oracle Database. This structure allows you to decide who will join the blockchain network, provides institutions and organizations with more customizability and better control.
All participants joining this network with the permissions granted must have privileges to add data to the Blockchain tables. Contents are defined and managed by Blockchain applications. This structure provides higher efficiency and lower transaction latency compared to non-blockchain architectures.
“Oracle Blockchain tables consists of rows added one after another, as in the Classic Blockchain tables. On the blockchain, every row depends on the previous row, except for the first row.”
However, rows in Blockchain tables are protected from manipulation compared to a conventional OLTP table. Each row is encrypted with a dependent hash to the data in the previous row.
If the data in a row changes, the HASH value of that row also changes. This also affects the HASH values of the rows after this row.
“Oracle BlockChain tables are recommended when the immutability of the data is critical for your central applications and you want to protect past transactions from manipulation.”
Benefits of Oracle BlockChain Tables
The use of blockchain tables provides the following benefits
- It provides transparent protection against manipulation by other participants in the blockchain network.
- Rows in the blockchain table are verified with HASH.
- Since it is part of the Oracle Database architecture, a new infrastructure is not required.
- It allows you to preserve the existing architecture and programming model. In this way, existing databases can be made more secure.
- It is easier to use compared to the distributed Blockchain architecture.
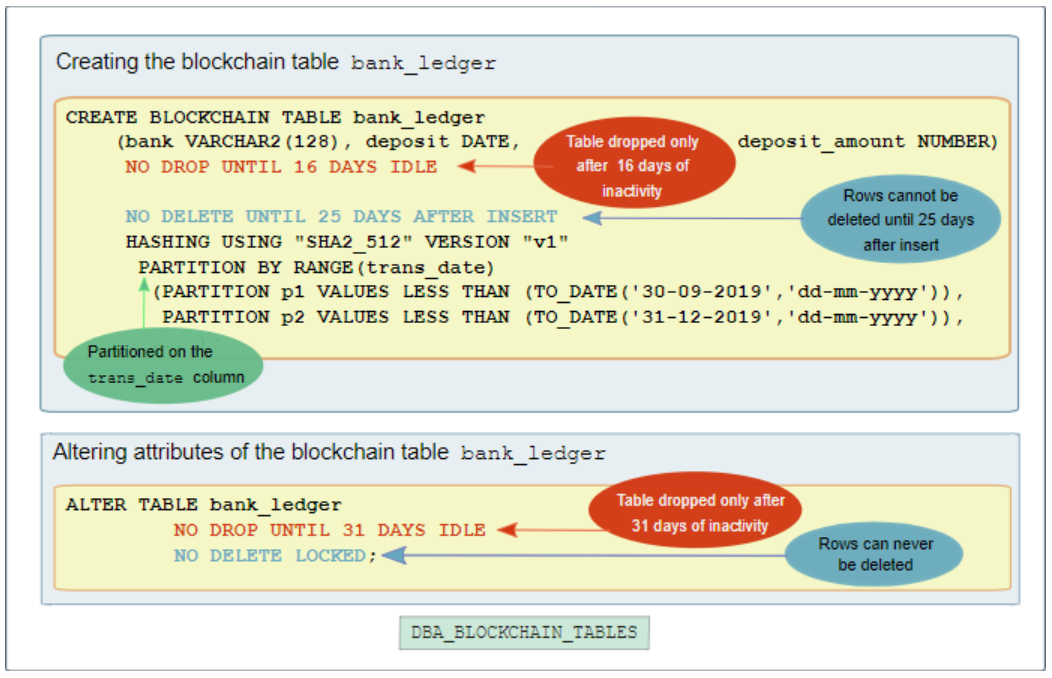
Blockchain tables are tables where insertions are allowed only. Deletion of rows is prohibited and restricted depending on the time.
Rows in Blockchain tables are made resistant to manipulation by special sorting and chain algorithms. Users can verify that the rows have not been changed. Hash values that are part of row metadata can be used to validate other rows.
Blockchain tables can be indexed and partitioned, as in classic database architecture. It can also be used in conjunction with classical tables.
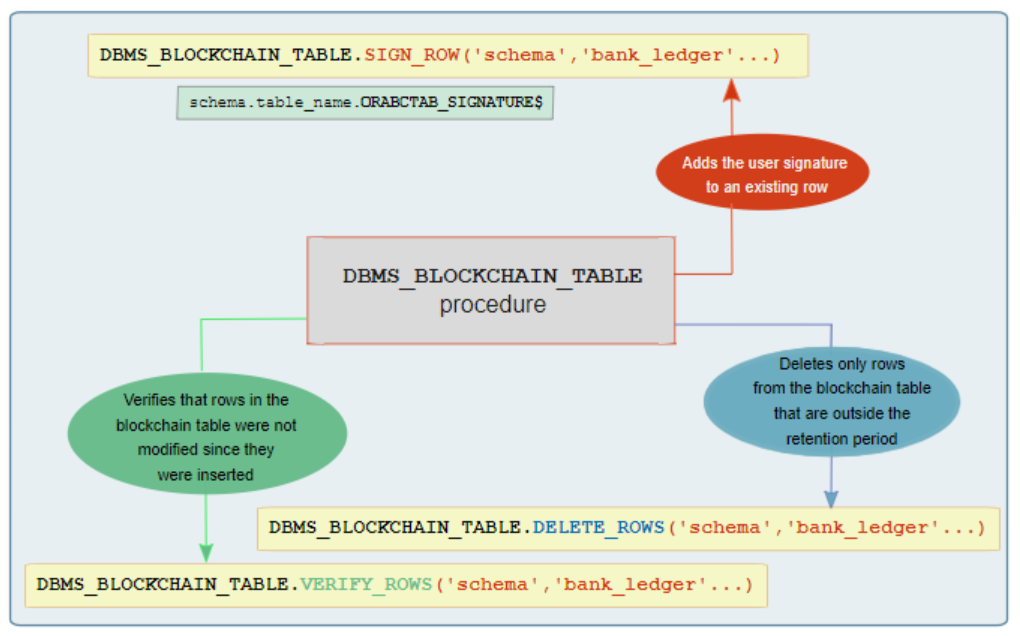
“Rows in blockchain tables can be signed by users.”
Oracle BlockChain Examples
Create BlockChain Table
A sample blockchain table creation method:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | SQL> CREATE BLOCKCHAIN TABLE ledger_emp (employee_id NUMBER, salary NUMBER) NO DROP UNTIL 31 DAYS IDLE NO DELETE LOCKED HASHING USING "SHA2_512" VERSION "v1"; Table created. SQL> |
Insert Data
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | SQL> INSERT INTO ledger_emp VALUES (106,12000); 1 row created. SQL> COMMIT; Commit complete. SQL> |
We started to Blockchain today, which is the technology of the future, maybe todays. Obviously, I want to experience this technology whenever I have time. I will share them with you as I gain experience.
Hope to see you again,
Resources:
https://docs.oracle.com/en/database/oracle/oracle-database/20/ftnew/practice-managing-oracle-blockchain-tables-and-rows.html
https://docs.oracle.com/en/database/oracle/oracle-database/20/ftnew/managing-oracle-blockchain-tables-and-data.html
https://blogs.oracle.com/blockchain/blockchain-tables-in-oracle-database:-technology-convergence
![]()
 Database Tutorials MSSQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL, MySQL, MariaDB, DB2, Sybase, Teradata, Big Data, NOSQL, MongoDB, Couchbase, Cassandra, Windows, Linux
Database Tutorials MSSQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL, MySQL, MariaDB, DB2, Sybase, Teradata, Big Data, NOSQL, MongoDB, Couchbase, Cassandra, Windows, Linux 