In today’s article, we will be learning the storage structure of Oracle Database.
Oracle Database storage structure consists of two structures: physical and logical.
The physical structure consists of files that we can physically see on the operating system.
The logical structure consists of logical concepts such as extent, segment, and tablespace within the oracle database structure, which we cannot physically see.
1. Database Blocks
It is the smallest unit of storage in the database.
A logical data block corresponds to operating system (OS) blocks.
Read/write operations in the database occur at the block level.
The size of a block is decided when the database is created and cannot be changed later. The size of the block depends on the DB_BLOCK_SIZE parameter in the parameter file. The default value is 8KB.
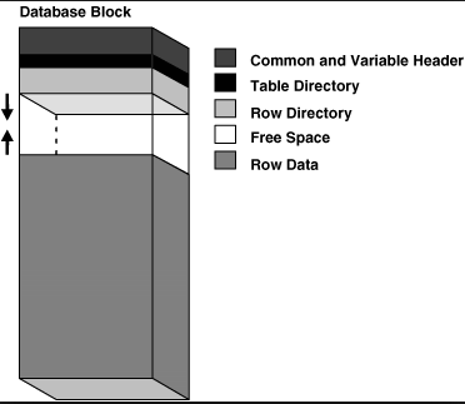
Header: Contains general block information such as block address.
Table Directory: Contains the table information of the data contained in the block.
Row Directory: Provides information about the actual rows in the block. It stores one address information for each line.
Row Data: The data located in the block is stored in this area.
Free Space: This is the additional space required for adding new rows or row updates.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | SQL> show parameter block NAME TYPE VALUE ------------------------------------ ----------- ------------------------------ db_block_buffers integer 0 db_block_checking string FALSE db_block_checksum string TYPICAL db_block_size integer 8192 db_file_multiblock_read_count integer 128 |
2.Extend
It is a storage set consisting of consecutive blocks. It consists of 8 blocks.
3. Segment
It is formed by the combination of extensions. When segments are mentioned, objects such as tables and indexes come to mind.
4. Tablespace
It is formed by the combination of segments.
![]()
 Database Tutorials MSSQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL, MySQL, MariaDB, DB2, Sybase, Teradata, Big Data, NOSQL, MongoDB, Couchbase, Cassandra, Windows, Linux
Database Tutorials MSSQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL, MySQL, MariaDB, DB2, Sybase, Teradata, Big Data, NOSQL, MongoDB, Couchbase, Cassandra, Windows, Linux 