In PostgreSQL, views are logical tables.
By turning queries into views we can use complex queries with a simple select statement.
For example, if you put a query that joins several tables into a view with view_x name, you can query this view with the following script.
1 | SELECT * FROM view_x; |
Thus, by running a complex query with a simple select expression, you reduce the complexity of the application.
We talked about the fact that the data are not physically stored in the views.
If you want to keep the data physically in view, you should create a materialized view.
For more detailed information on materialized views, you may want to read the article entitled “How To Create a Materialized View On PostgreSQL“.
Below is a simple example of using views.
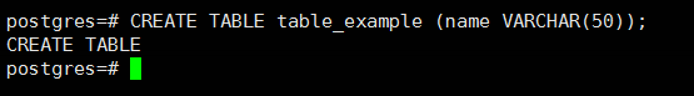
First, we create a table with the help of the following script.
1 | CREATE TABLE table_example (name VARCHAR(50)); |
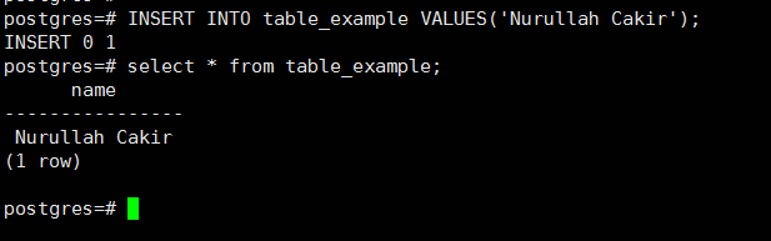
We then add a record to this table with the help of the following script and then query the table to check it later.
1 | INSERT INTO table_example VALUES('Nurullah Cakir'); |
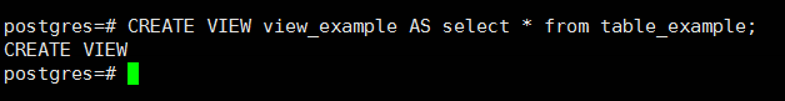
Then we create a view that queries this table with the help of the following script.
1 | CREATE VIEW view_example AS select * from table_example; |
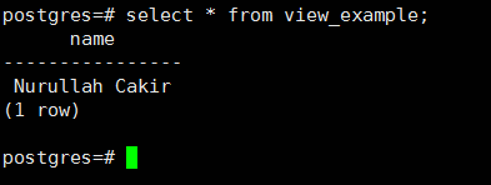
You can then query the view as follows.
1 | select * from view_example; |
How do we alter views?
First, let’s add a column to the table.
1 | ALTER TABLE table_example ADD COLUMN city VARCHAR(50); |
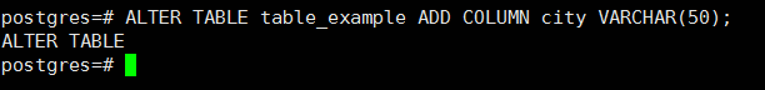
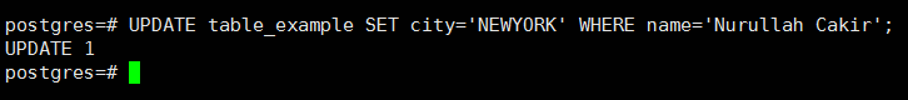
Later we will update the table to fill in the column we added.
1 | UPDATE table_example SET city='NEWYORK' WHERE name='Nurullah Cakir'; |
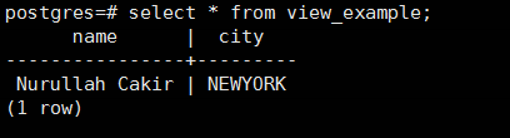
Let’s check the contents of the view again with the following select script.
1 | select * from view_example; |
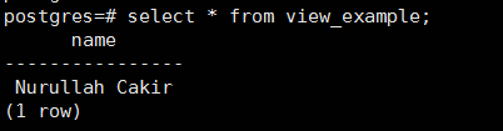
The city column did not come as you see it.
Because there was no such column when we created the view.
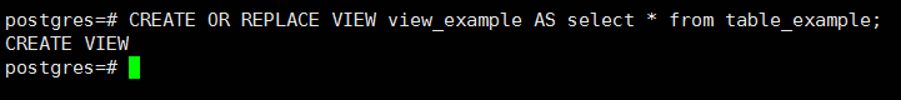
Now we update the view with the following script and then check again.
1 | CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW view_example AS select * from table_example; |
1 | select * from view_example; |
Let’s try to delete a column from the View.
1 | CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW view_example AS Select name from table_example; |
![]()
We got an error like you saw it. “can not drop columns from view”
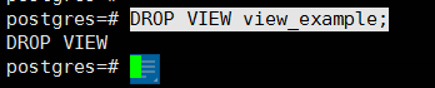
You can delete and recreate the view as follows.
1 | DROP VIEW view_example; |
You may want to look at the following articles about Views.
“How To Create a Materialized View On PostgreSQL“,
“How To Create a Recursive View On PostgreSQL“,
“How To Create an Updateable View On PostgreSQL“,
“How To Create an Updateable View WITH CHECK CONSTRAINT On PostgreSQL“
![]()
 Database Tutorials MSSQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL, MySQL, MariaDB, DB2, Sybase, Teradata, Big Data, NOSQL, MongoDB, Couchbase, Cassandra, Windows, Linux
Database Tutorials MSSQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL, MySQL, MariaDB, DB2, Sybase, Teradata, Big Data, NOSQL, MongoDB, Couchbase, Cassandra, Windows, Linux 