In this article, we will examine the settings that should be done on a Numa Node system. You must make these settings on systems that do not have a numa node. The reason we enter the subject with Numa Node is that these settings become more critical in Numa Node systems.
When the number of CPUs and clock speed(Clock speed is the smallest moment slice the processor can handle a command. Processor can complete a process in a shorter time with increased clock speed) increases in a system, the bottlenecks in Memory begin.
Due to the increased CPU and clock speed, the processes become a contention on a single memory bus. Therefore, some waiting starts to happen in memory.
Numa is designed to prevent this. If we go through an example, consider a system with 64 CPUs. Suppose we have eight nodes in the system. In this way, there are 8 CPUs on each numa node. And a special memory is allocated for each numa node. This special memory space allocated for numa nodes is called local memory. The memory on the other nodes is called foreign memory. And each numa node has its own memory bus.
Each numa node has its own CPU and memory, so there is no memory bottleneck.
I listed below what should be done in a Numa Node system:
MAX SERVER MEMORY and MIN SERVER MEMORY
The values of these two parameters must be the same.
In this way, memory allocate and deallocate operations will not be performed on SQL Server.
When you set MAX SERVER MEMORY, SQL Server distributes the memory evenly to numa nodes. And this will affect the performance of queries by reducing the Foreign Page requirement.
If you are using more than one instance on the server, you should pay attention to the sum of the memory that the instance uses when setting the lock pages in memory and MIN SERVER MEMORY.
If the operating system does not have enough RAM, the memory bottleneck may occur and the server may restart. If reporting services, analysis services are running on the database server, or if applications and database are on the same server, you need to pay more attention to this. (This is not recommended at all)
Before setting these parameters, you can check the amount of ram used by applications / services from the Resource Monitor.
In order to avoid memory bottlenecks in the operating system, you should follow the Available Mbytes perfmon counter. In this way, you can find the application / service that causes the Memory bottleneck and block the bottleneck in the Operating System.
Lock Pages In Memory
For the Lock pages in memory parameter, the SQL Server Service account must be granted on Windows.
With this feature, SQL Server does not give the memory that it allocates from windows.
Lock pages in memory is a feature on Windows. You should reserver the required amount of ram to the windows when you set Lock pages in memory.
You can give the required permission to the SQL Server service account on windows as follows.
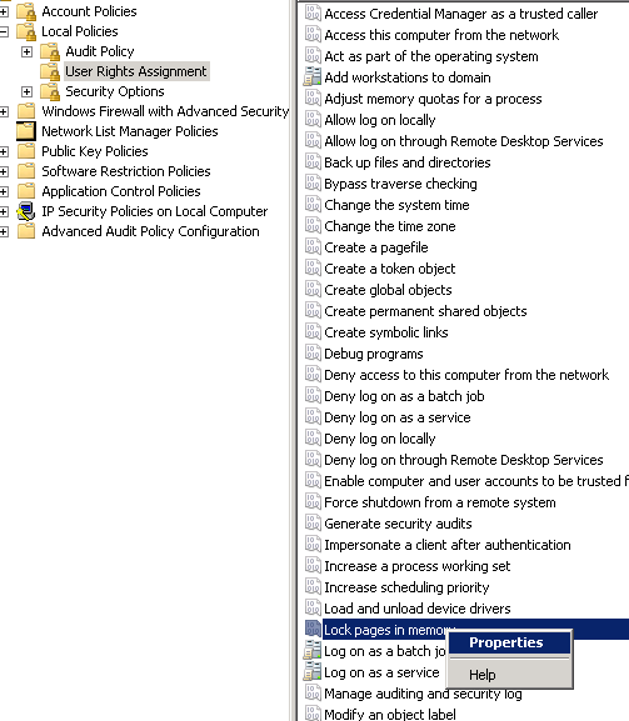
First type secpol.msc for Local Security Policy. Then go to the Local Policies/User Rights Assignment.
Right click to the Lock pages in memory and add sql server service account.
MAXDOP
The MAXDOP value must not exceed the number of CPUs on each numa node. This ensures that all numa nodes work more efficiently simultaneously.
If the MAXDOP does not exceed the cpu number in the numa node, the incoming query will probably use local memory. And this will affect the performance of queries by reducing the Foreign Page requirement. Of course, this does not mean that MAXDOP should be set as much as the number of CPUs in the numa node. The MAXDOP setting should be based on the type of system.
In OLTP systems, this value is usually 1. As an important detail, MAXDOP should not be set to 0. Because when it is 0, it means that query can run as parallel as the number of CPUs on the server.
With the following query, you can learn Foreign Node Memory, Free Node Memory and Total Node Memory for SQL Server 2012.
1 2 3 | select counter_name , cntr_value/1024 memory_mb, instance_name,*from sys.dm_os_performance_counters where [object_name] like '%SQLServer:Memory Node%' |
You must first run the above script without the where condition.
You should then determine what to write to where SQLServer is written, and then run it using the where condition.
![]()
 Database Tutorials MSSQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL, MySQL, MariaDB, DB2, Sybase, Teradata, Big Data, NOSQL, MongoDB, Couchbase, Cassandra, Windows, Linux
Database Tutorials MSSQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL, MySQL, MariaDB, DB2, Sybase, Teradata, Big Data, NOSQL, MongoDB, Couchbase, Cassandra, Windows, Linux 