Docker, which is becoming increasingly popular, is in the logic of virtualization. But unlike conventional known virtualization tools(Virtualbox, Vmvare ,kvm vb.. ), it does not use the Hypervisor layer. Docker serves using the Docker Engine structure instead of hypervisor layer.
If we talk about the concept of hypervisor briefly; it is a code piece that enables virtualization to run on physical machines. It helps us run multiple guest operating systems on the physical server.

After sharing summary information about Hypervisor and Docker, we can start installing Docker on Centos 7.
We need to install the following dependencies before installing the Docker.
- yum-utils
- device-mapper
- device-mapper-persistent-data
- lvm2
1 2 3 | yum install -y yum-utils \ device-mapper-persistent-data \ lvm2 |
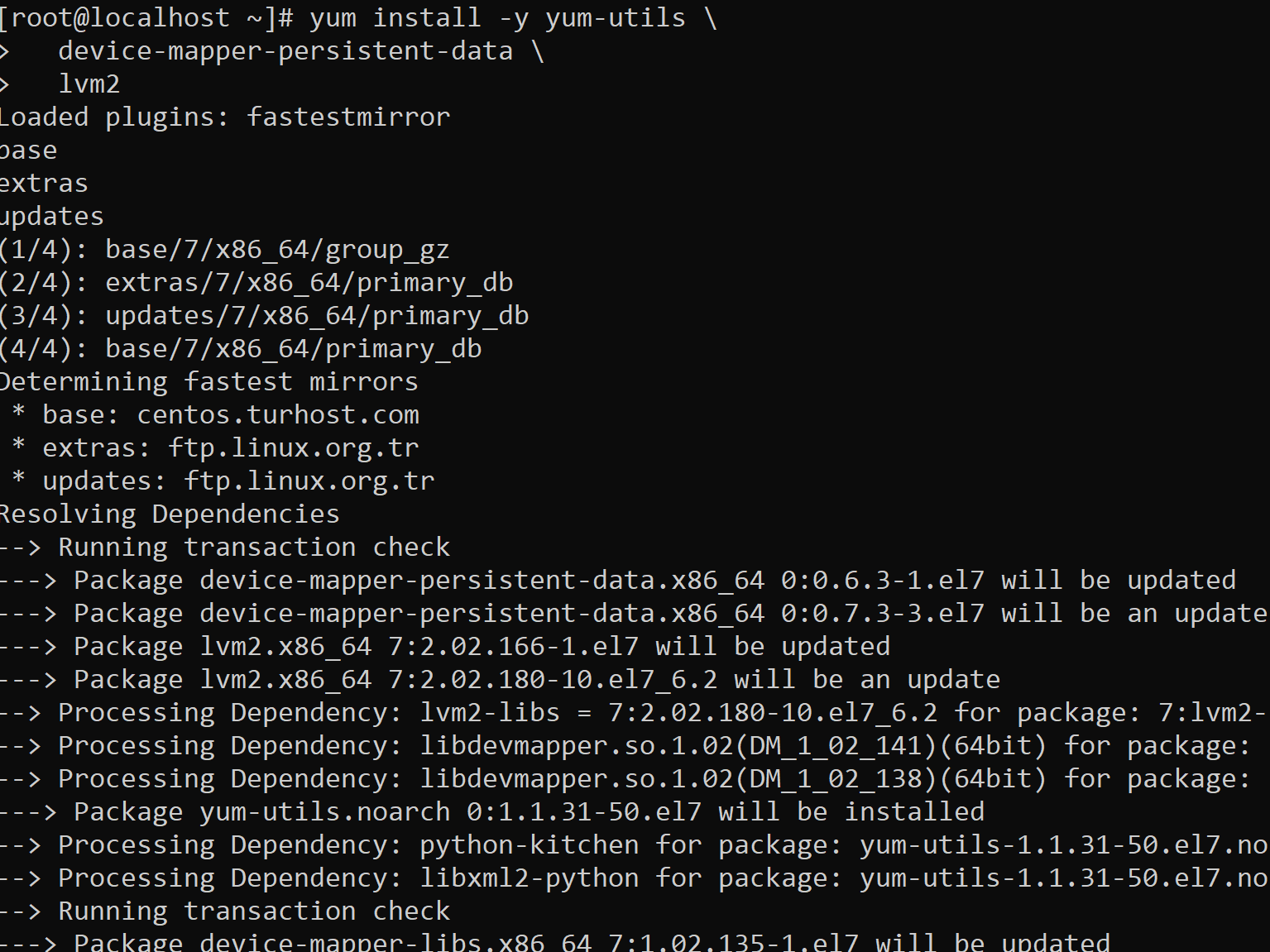
After the dependent packages are installed, we add the repo of the docker to the current repo as follows.
1 2 3 | yum-config-manager \ --add-repo \ https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo |
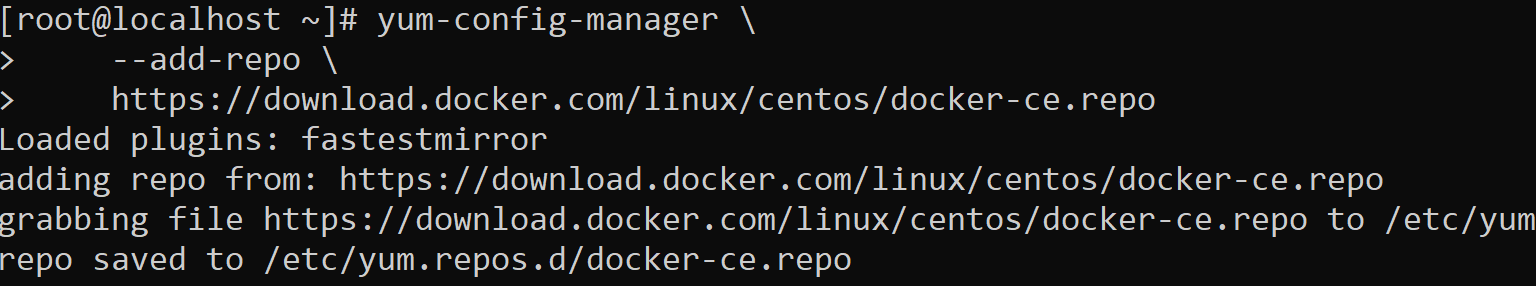
After the repo of the docker is added to the current repo, we can list the versions of the docker in the repository as below.
1 | yum list docker-ce --showduplicates | sort -r |
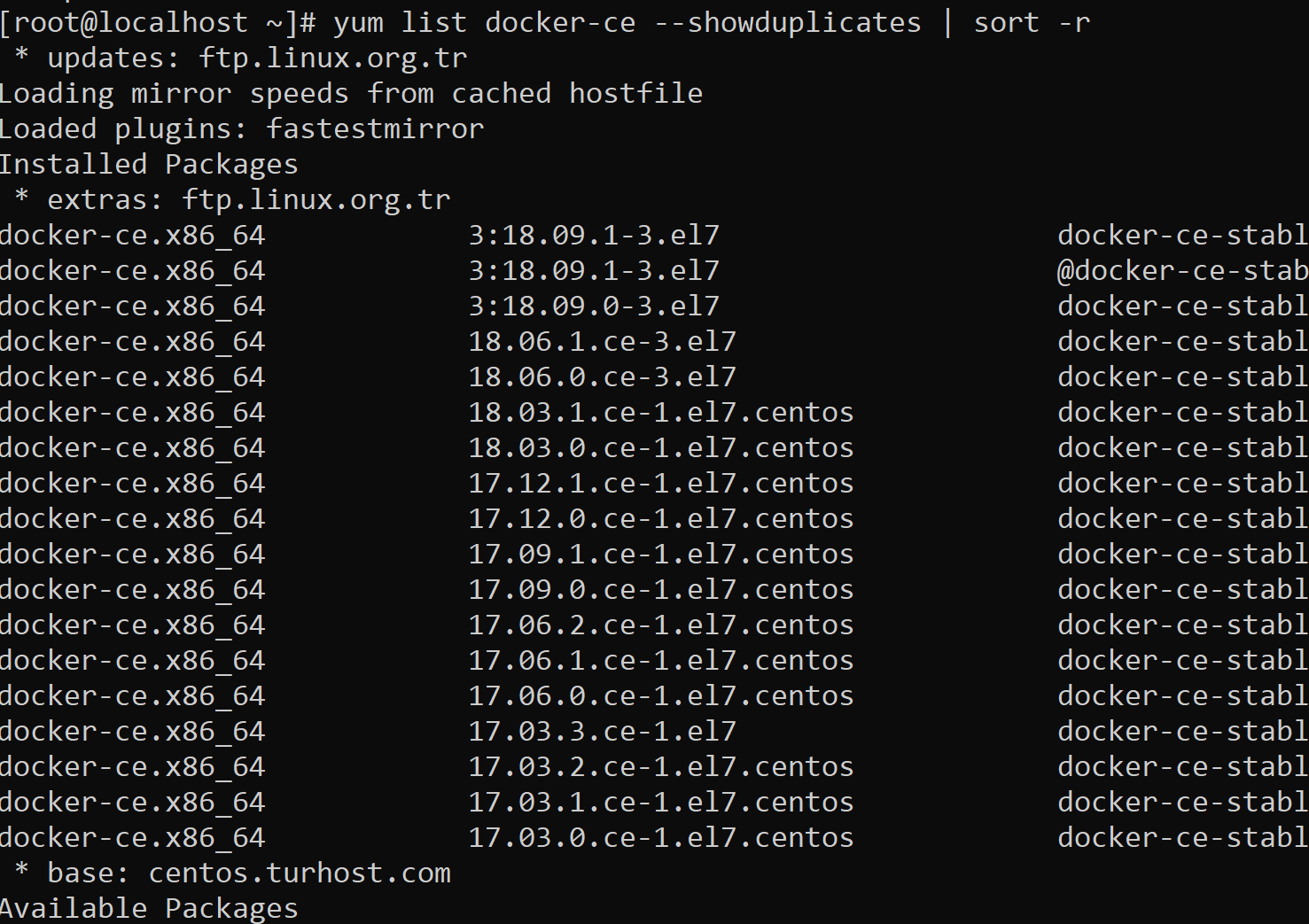
We can install the version we want according to the following syntax.
1 | yum install docker-ce-<Version> |
You can use the following command to install the most up-to-date dock version in the repo without specifying a version.
1 | yum install docker-ce |
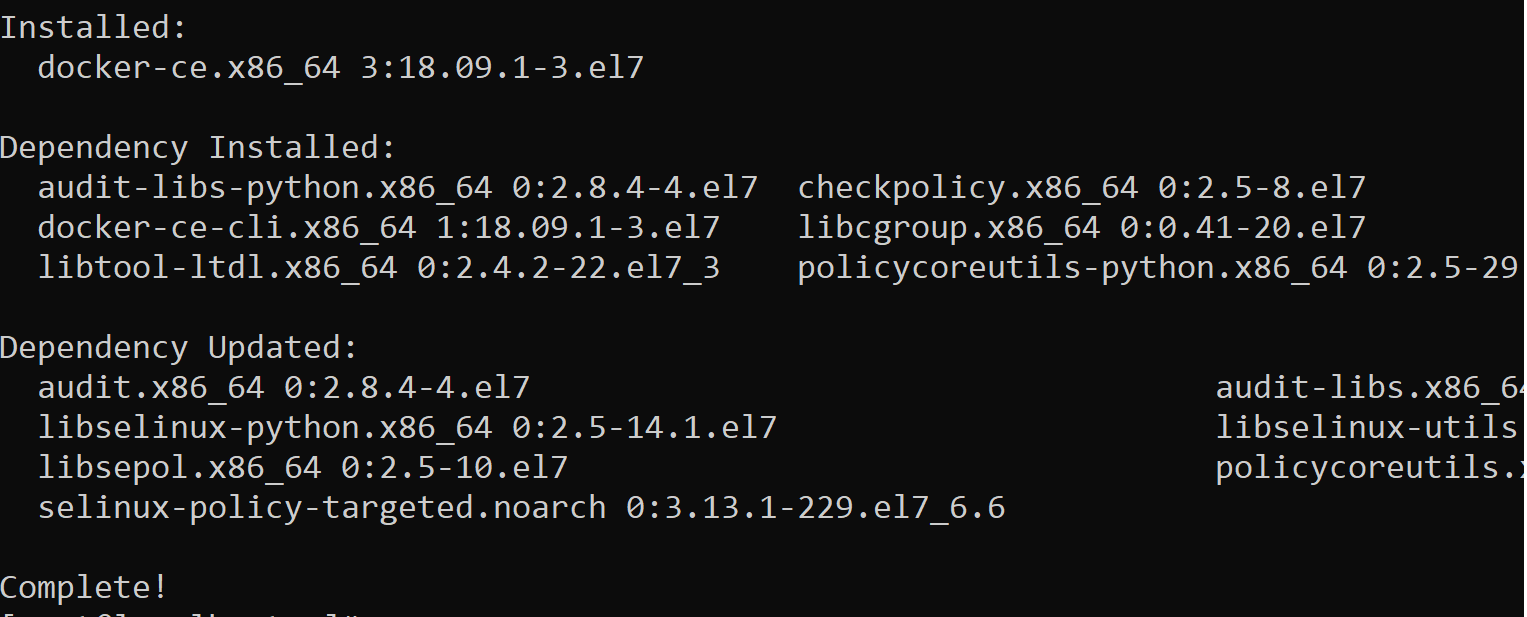
After running the command, you can see that the docker and dependencies are installed as above.
We use the following command to start the Docker service.
as root:
1 | systemctl start docker |
If we want to check the status of the service, we can use the following command.
1 | systemctl status docker |
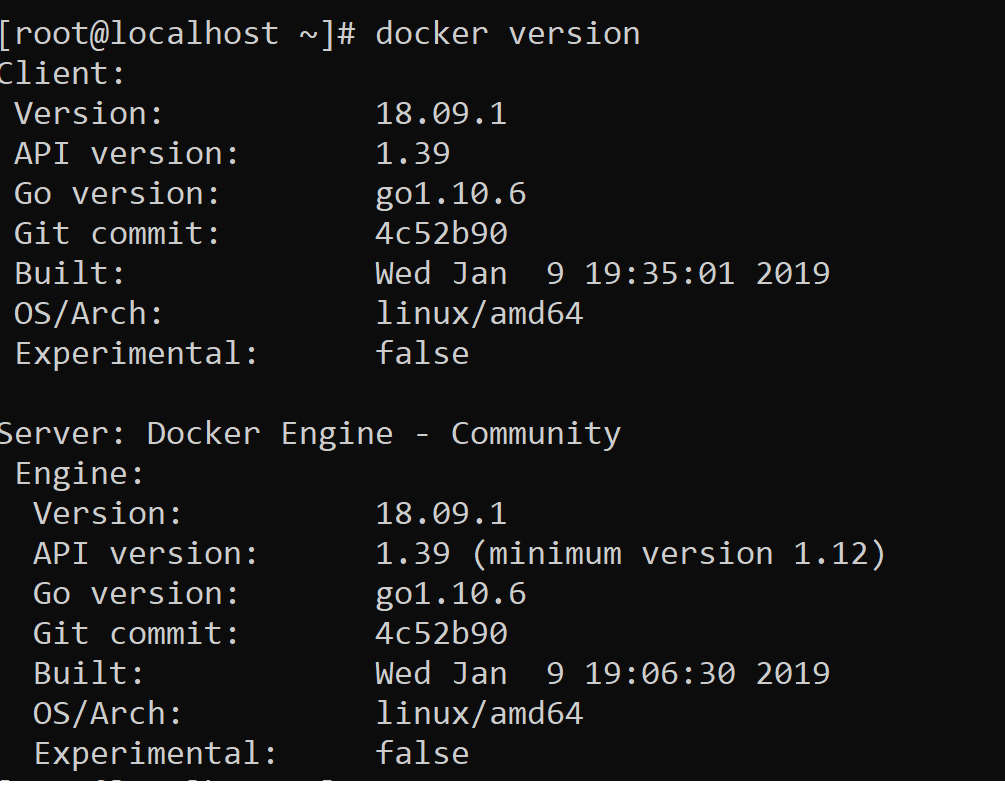
You can use the following command to learn the version of Docker.
1 | docker version |
![]()
 Database Tutorials MSSQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL, MySQL, MariaDB, DB2, Sybase, Teradata, Big Data, NOSQL, MongoDB, Couchbase, Cassandra, Windows, Linux
Database Tutorials MSSQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL, MySQL, MariaDB, DB2, Sybase, Teradata, Big Data, NOSQL, MongoDB, Couchbase, Cassandra, Windows, Linux 
Why do we have to add docker-ce when docker is already available in yum? I can’t find this explained anywhere.