In today’s article, we will examine Data Guard Protection Modes.
Data Guard Protection Modes are a decision that we can make by looking at how valuable the data is to us or how important the continuity of the primary database is. Therefore, we cannot define Redo Transport mode as a stand-alone data protection mode.
We have 3 types of Protection Modes in Oracle.
Maximum Protection
Maximum Availability
Maximum Performans
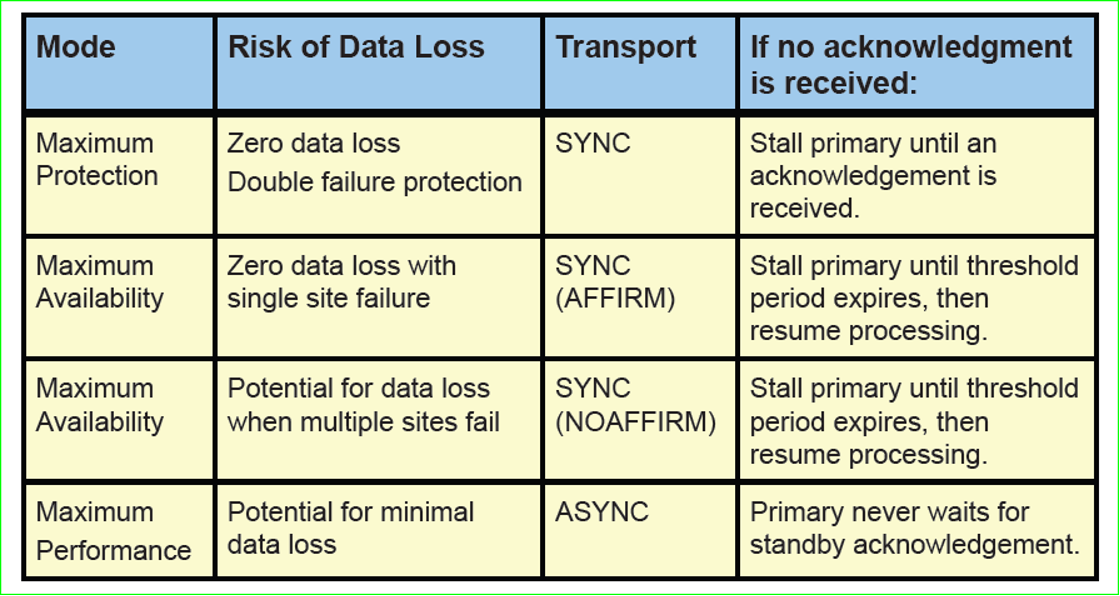
Maximum Protection
It guarantees us zero data loss against the problems we may encounter in Primary Database, network or all standby databases.
It does this by closing the Primary Database when it realizes that it cannot write Redo even to at least one standby database that we run synchronously.
Therefore, Redo information in Maximum Protection mode is written to at least one standby database that works synchronously with the local online redo log.
In order to provide this information, at least one standby database must have Standby Redo Logs or the LOG_ARCHIVE_DEST_n parameter must have SYNC and AFFIRM Redo Transport features.
Oracle recommends using Maximum Protection mode in a Data Guard Environment with at least 2 Standby Databases.
Far does not support SYNC Maximum Protection mode because it has SYNC and NOAFFIRM working logic.
Maximum Availability
It guarantees us zero data loss without compromising the availability of the Primary Database.
It does this by not committing the transaction unless the Redo information is both written to the local online redo log file and Stanby is sure that the RFS process running on the side receives the redo information.
Therefore, we cannot expect the disk I/O to be instantiated and an acknowledge to the Primary. It provides the availability of the primary by not closing the primary database in case of communication problem between the standby and the primary for some reason at that moment.
Asynchronous operation continues until the communication problem is resolved and the GAP is closed. When the GAP is closed, it automatically continues to work synchronously.
In order to provide this information, at least one of our standby database must have Standby Redo Logs and our LOG_ARCHIVE_DEST_n parameter must have SYNC and NOAFFIRM Redo Transport properties.
Maximum Performance
It is the default Data Protection mode.
It is based on the primary database working with maximum performance.
It does this by committing transactions as soon as our redo information is written to the local online redo log.
Therefore, our redo information is sent to the Standby side asynchronously.
In order to provide this information, at least one standby database must have Standby Redo Logs and the LOG_ARCHIVE_DEST_n parameter must have ASYNC and NOAFFIRM Redo Transport properties.
If we don’t have a problem in the network, our system can work like Maximum Availability mode even when using this mode.
If we want to ENABLE Fast-Start Failover, we must use Maximum Availability or Maximum Performance mode.
Comparison of Our Data Protection Modes
![]()
 Database Tutorials MSSQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL, MySQL, MariaDB, DB2, Sybase, Teradata, Big Data, NOSQL, MongoDB, Couchbase, Cassandra, Windows, Linux
Database Tutorials MSSQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL, MySQL, MariaDB, DB2, Sybase, Teradata, Big Data, NOSQL, MongoDB, Couchbase, Cassandra, Windows, Linux 